Intron
Definition
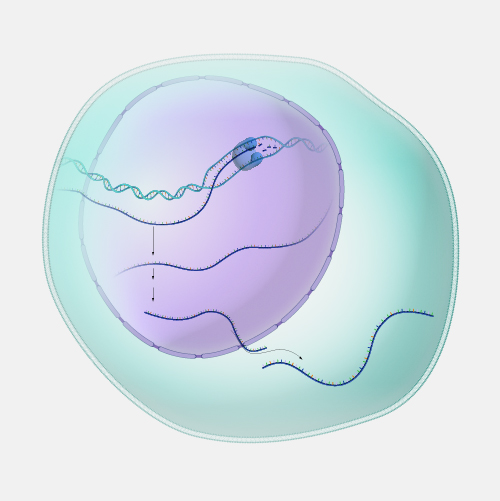
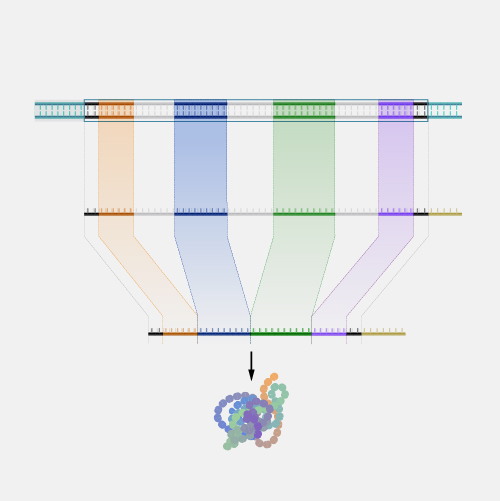
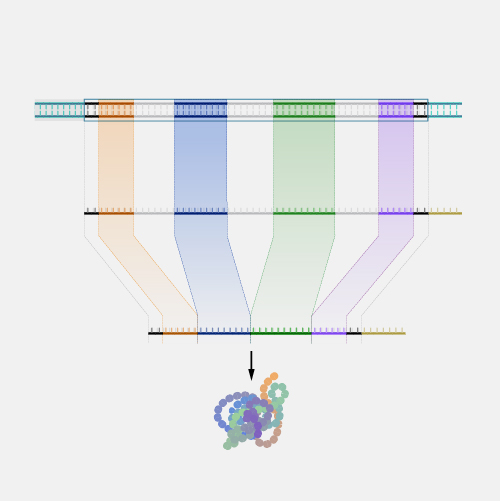
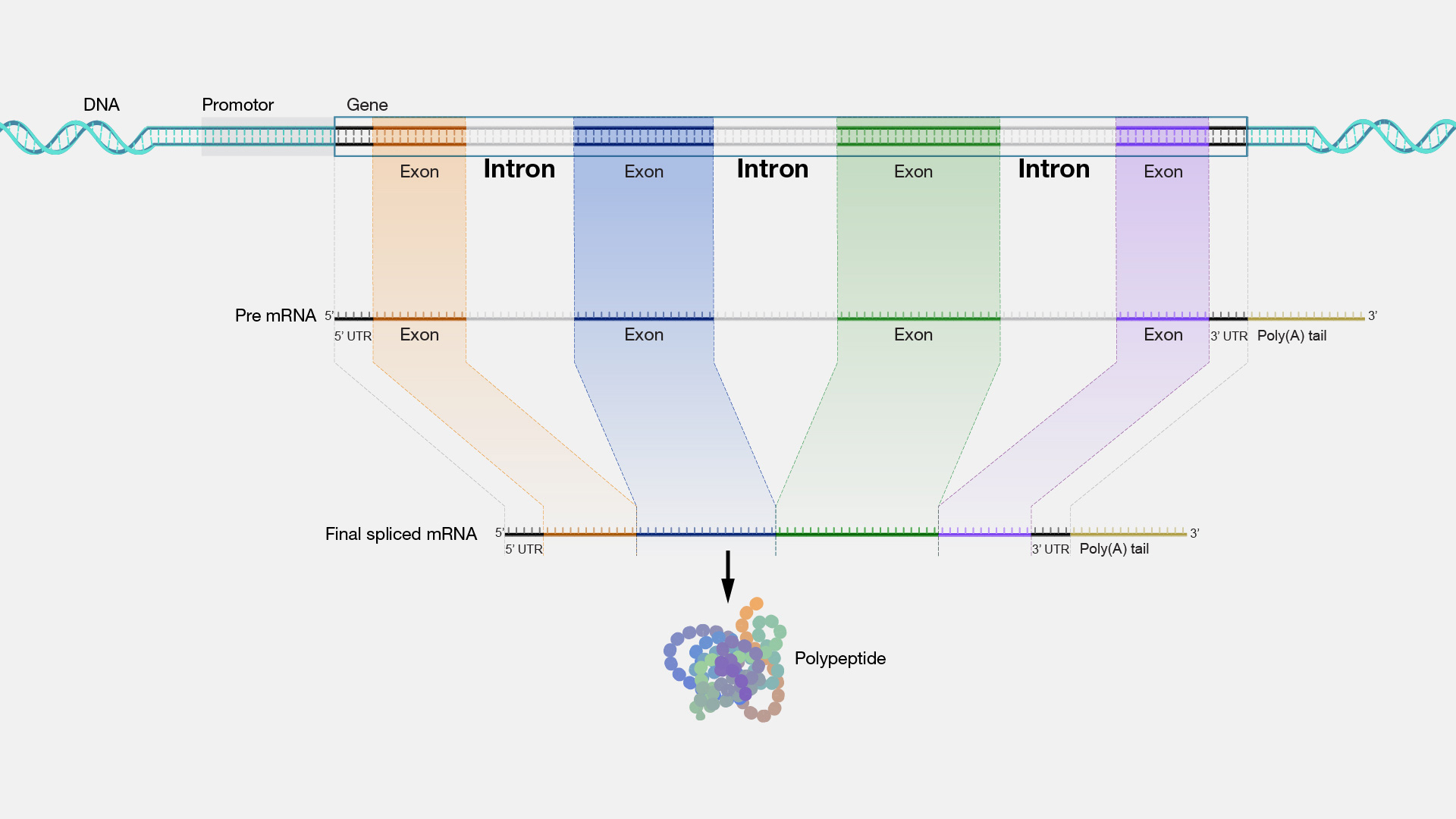
An intron is a region that resides within a gene but does not remain in the final mature mRNA molecule following transcription of that gene and does not code for amino acids that make up the protein encoded by that gene. Most protein-coding genes in the human genome consist of exons and introns.
Narration
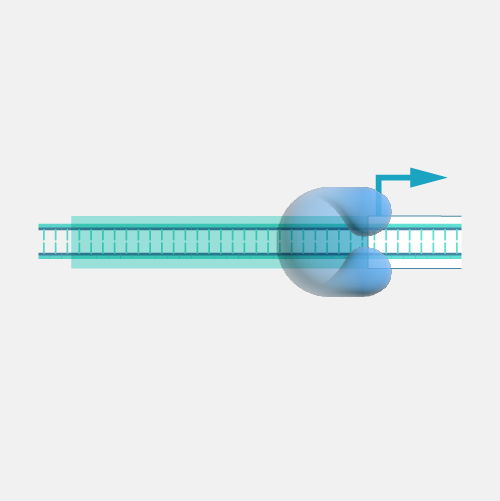
Intron. The protein coding sequences for many genes are broken into smaller pieces of coding sequences called exons separated by non-coding sequences called introns. When genes are transcribed, those exons and introns are included in the initial messenger RNA products. However, introns are removed during the process called splicing so only exons are included in the mature mRNA and used to dictate what proteins are produced. In many genes, the introns are much longer than the exons. Introns may contain sequences that regulate how genes are expressed or transcribed and how mRNA is processed.