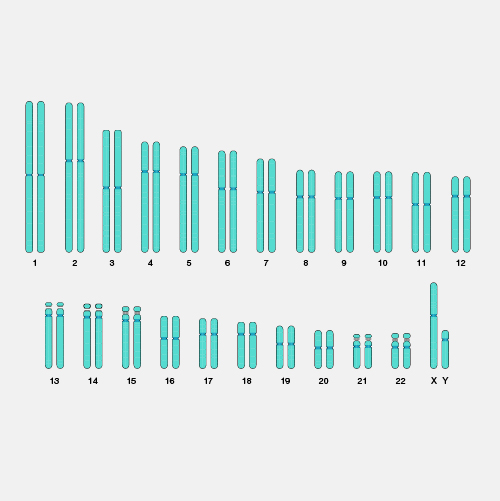
Somatic Cells
Definition
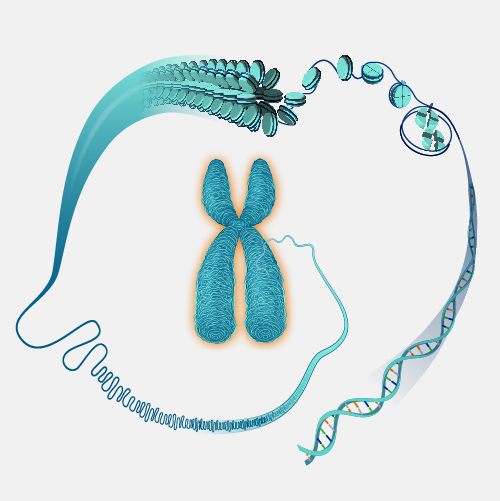
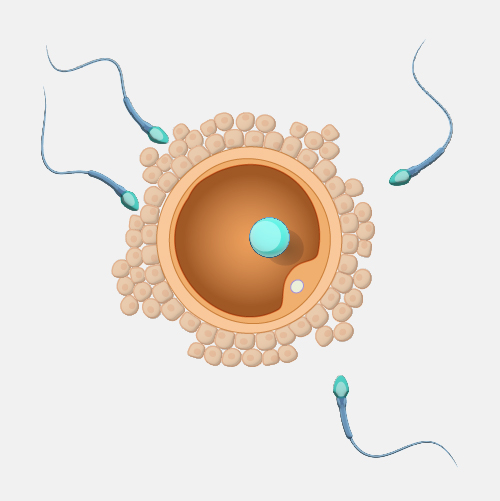
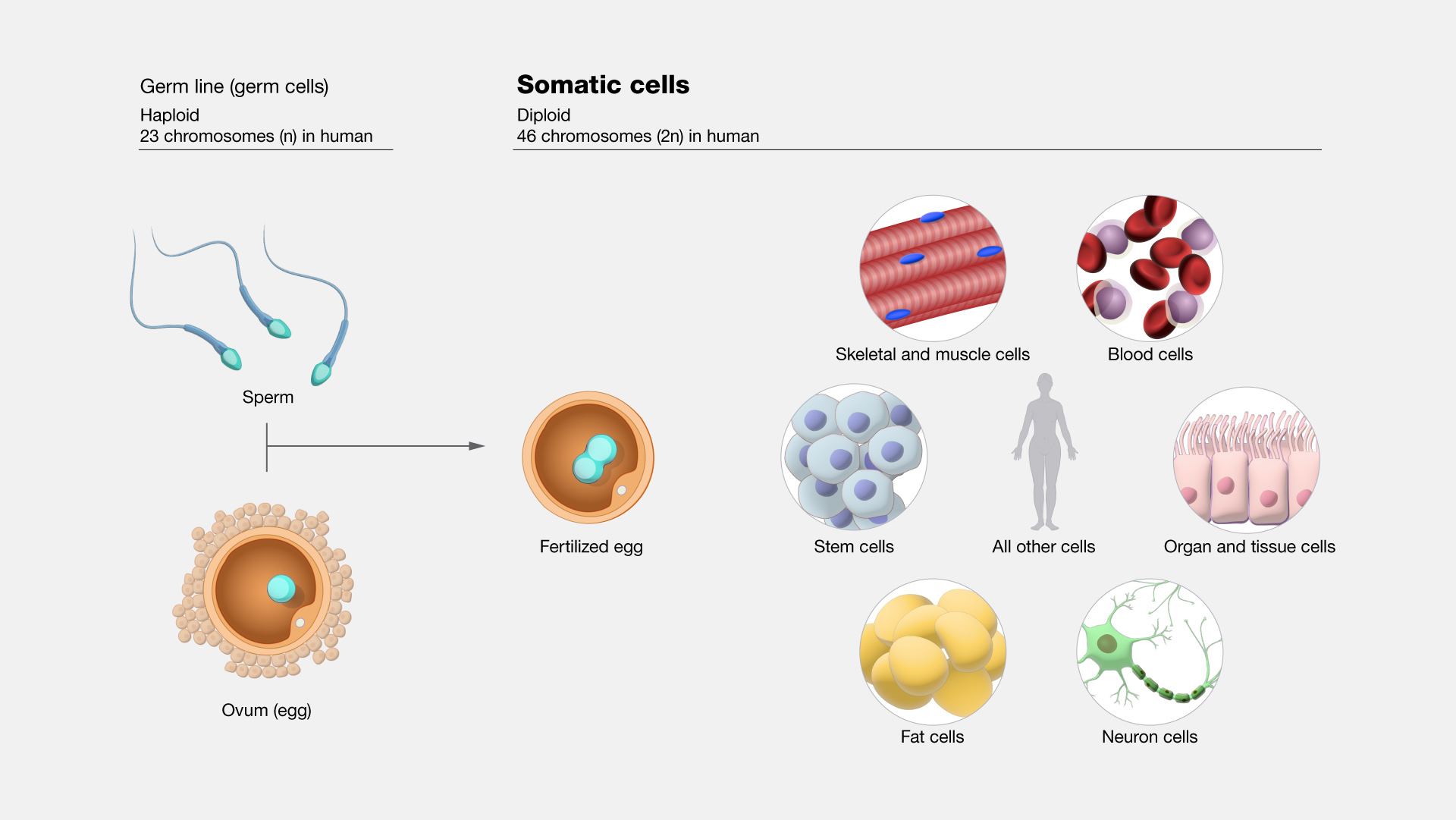
Somatic cells are the cells in the body other than sperm and egg cells (which are called germ cells). In humans, somatic cells are diploid, meaning they contain two sets of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent. DNA mutations in somatic cells can affect an individual, but they cannot be passed on to their offspring.
Narration
Somatic cells. All organisms that are alive are made of one or more cells that are called somatic cells. In humans, somatic cells are diploid, meaning they contain two sets of chromosomes, one set inherited from each parent. Somatic mutations can impact the individual carrying the mutation, but cannot be passed on and have no effect on the offspring.