Carcinogen
Definition
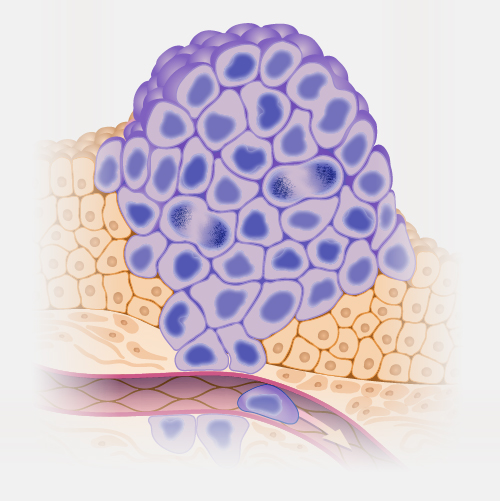
A carcinogen is a substance, organism or agent capable of causing cancer. Carcinogens may occur naturally in the environment (such as ultraviolet rays in sunlight and certain viruses) or may be generated by humans (such as automobile exhaust fumes and cigarette smoke). Most carcinogens work by interacting with a cell’s DNA to produce mutations.
Narration
Carcinogen. A carcinogen is any substance that can cause cancer. It's important to identify items that might be carcinogenic because we can then take specific measures to avoid or limit our exposure to them. The US Department of Health and Human Services National Toxicology Program, and the World Health Organization's International Agency for Research on Cancer both use evidence-based approaches to catalog substances that are known or reasonably anticipated to be human carcinogens. Both use evidence-based approaches to catalog substances that are known or are reasonably anticipated to be human carcinogens. To date, over 500 substances have been identified as definitive, probable, or possible carcinogens for humans. This includes items like asbestos, automobile exhaust, processed meat, or ultraviolet rays. I should stress that exposure to a carcinogen does not necessarily mean you will get cancer. A number of factors influence whether a person exposed to a carcinogen will ultimately develop cancer, including the amount and duration of the exposure, exposure to other environmental factors, and the individual's genetic background.