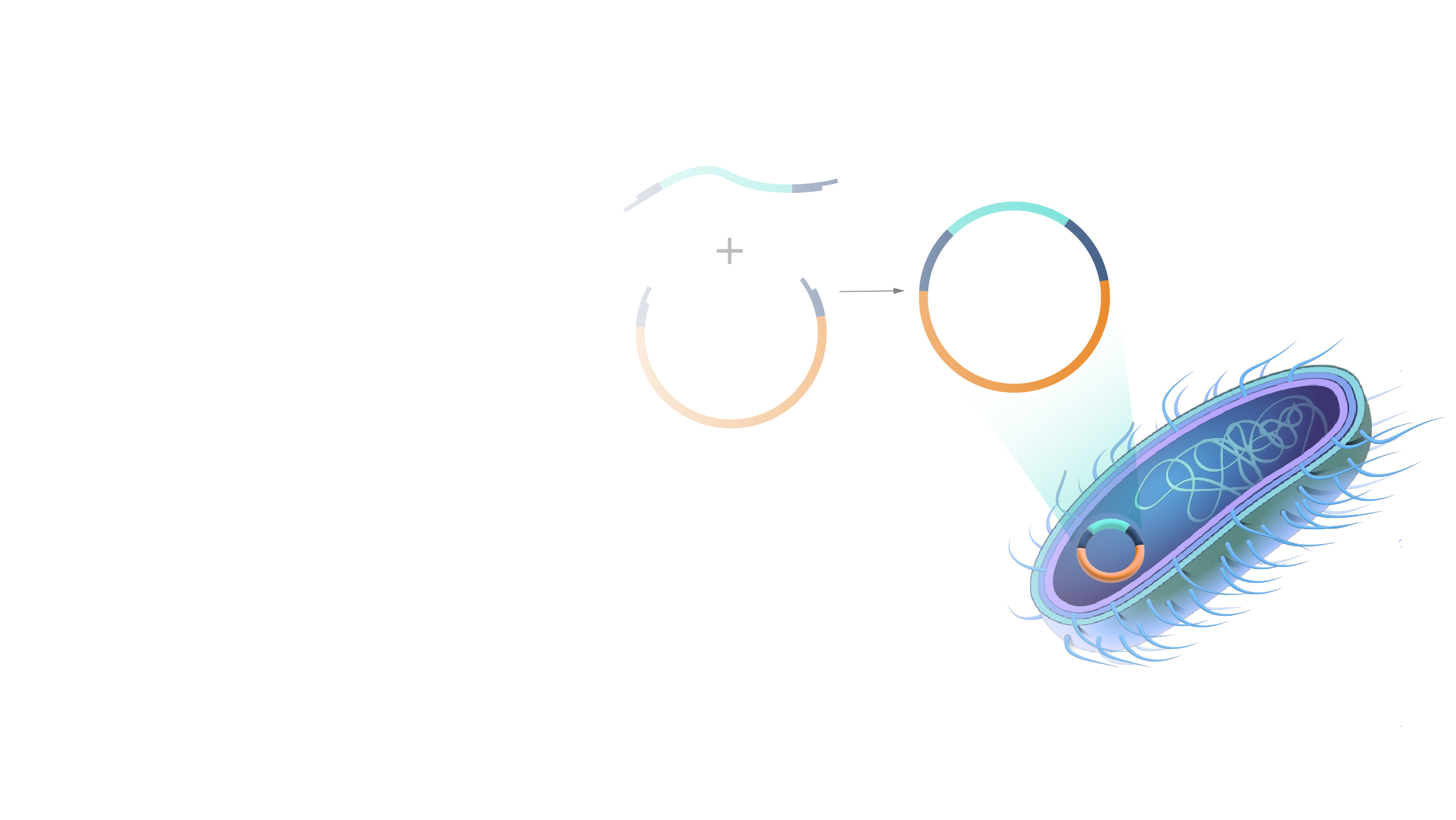
Restriction Enzyme
Definition
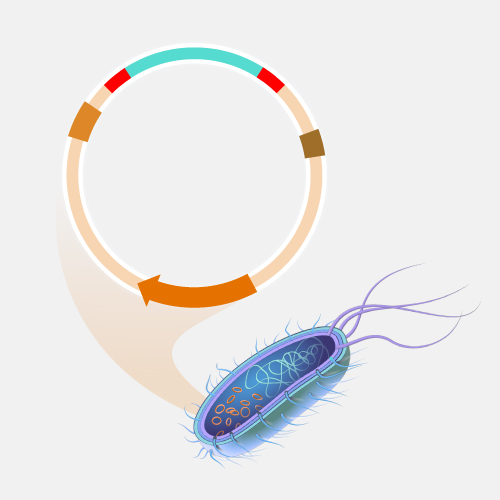
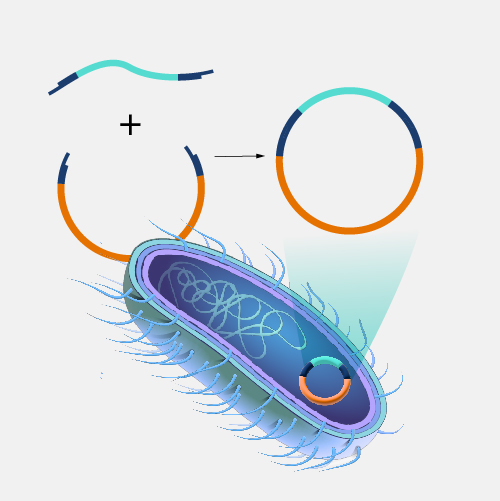
A restriction enzyme is a protein isolated from bacteria that cleaves DNA sequences at sequence-specific sites, producing DNA fragments with a known sequence at each end. The use of restriction enzymes is critical to certain laboratory methods, including recombinant DNA technology and genetic engineering.
Narration
Restriction enzyme. Restriction enzymes are incredibly cool, and there are at least three thousand of them. Each one of these enzymes cuts a specific DNA sequence and doesn't discriminate as to where the DNA comes from — bacteria, fungi, mouse, or human, snip, snip, snip.