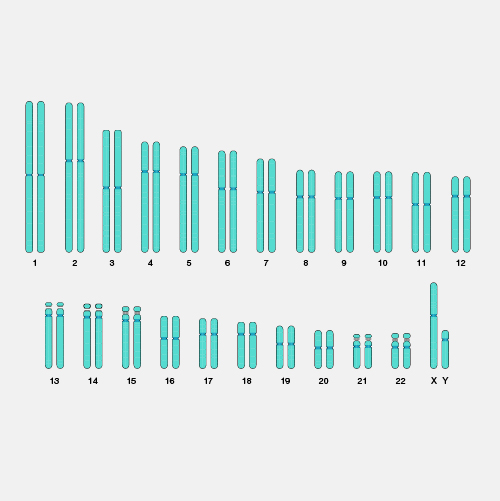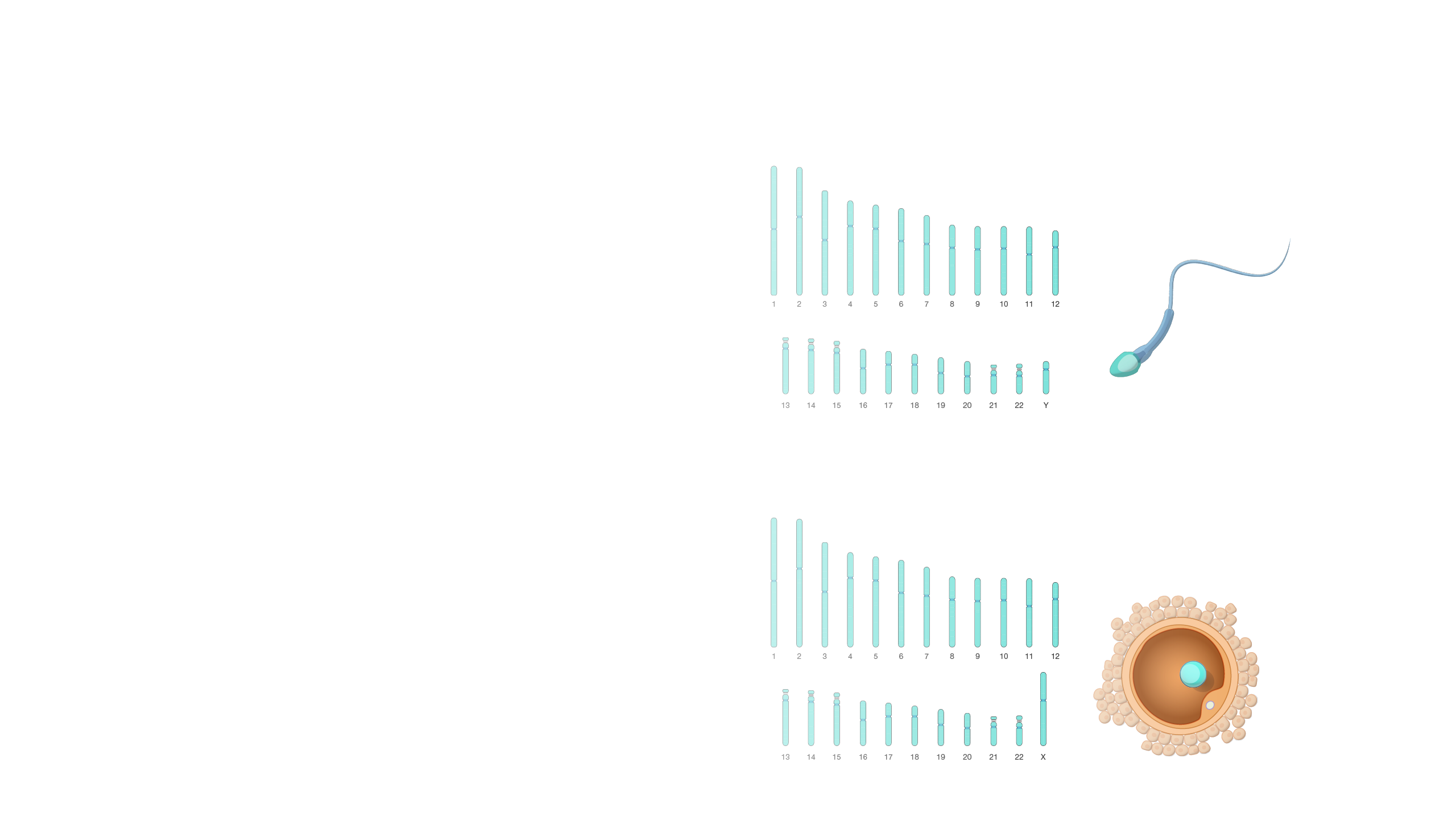
Haploid
Definition
Haploid refers to the presence of a single set of chromosomes in an organism’s cells. Sexually reproducing organisms are diploid (having two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent). In humans, only the egg and sperm cells are haploid.
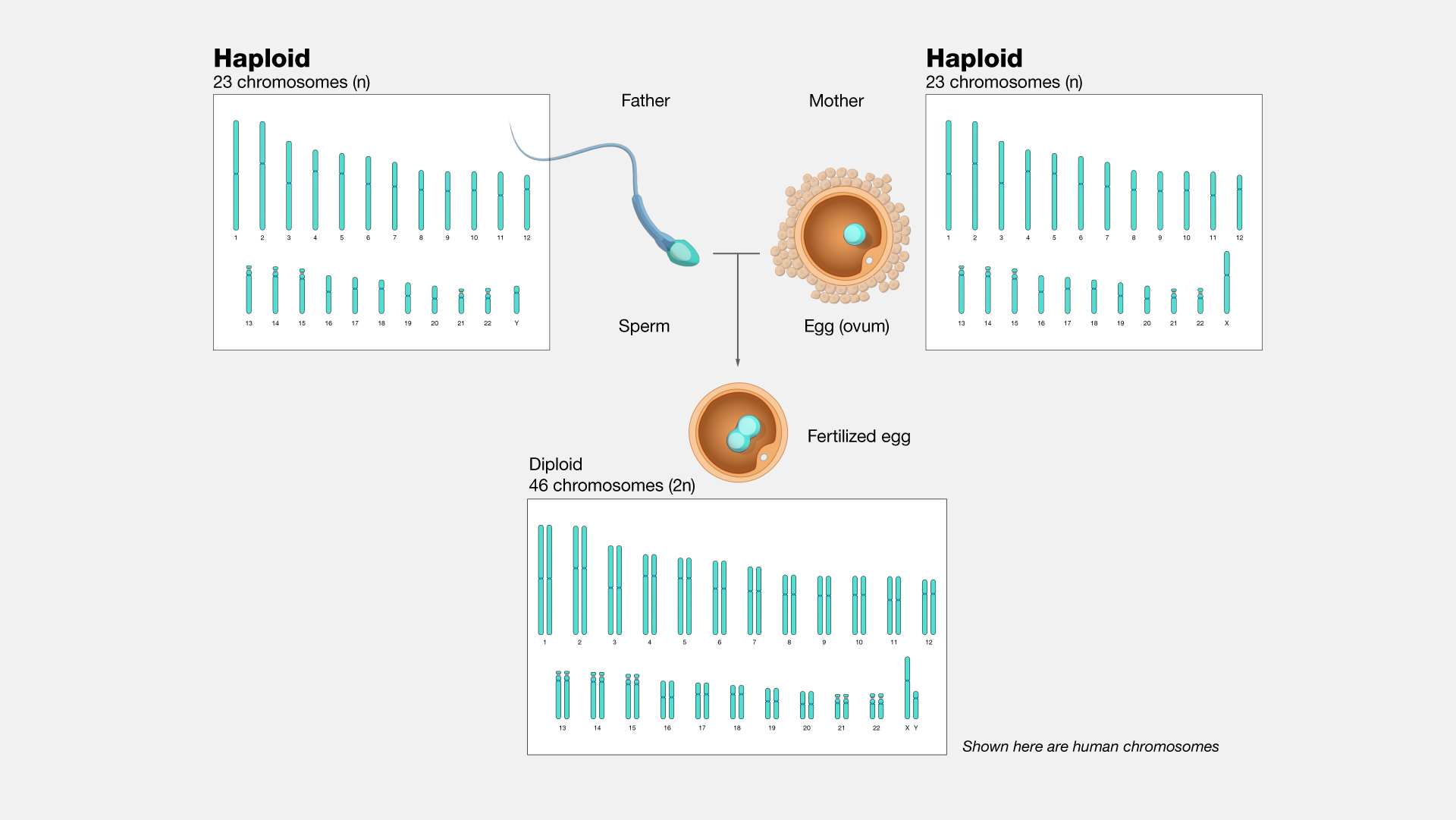
Narration
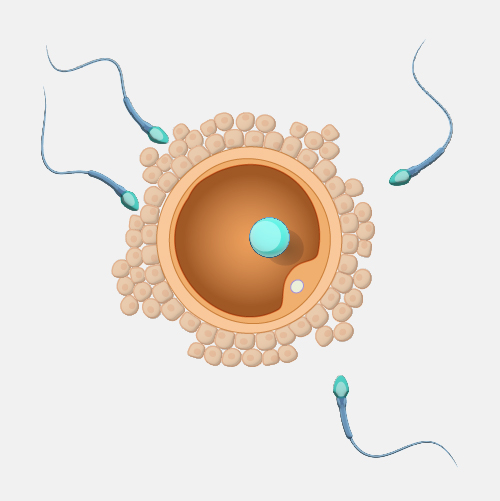
Haploid. A haploid cell has only a single set of chromosomes. Most cells in humans are diploid rather than haploid, meaning they have two copies of each chromosome. In humans, the egg and sperm cells are formed through a particular kind of cell division called meiosis where the genetic material of the parent cell is divided up twice, resulting in these haploid cells with only one set of chromosomes. When a sperm fertilizes an egg, the genetic material is combined in the resulting zygote cell. In other words, a single set of chromosomes in two separate haploid cells come together as two sets of chromosomes in a single diploid cell. That zygote cell ultimately undergoes development into a new person. Interestingly in some insect species including wasps, bees, and ants, the males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid while the females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid.