Chromatin
Definition
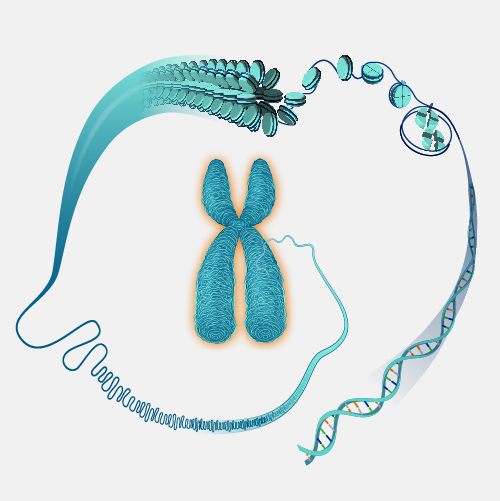
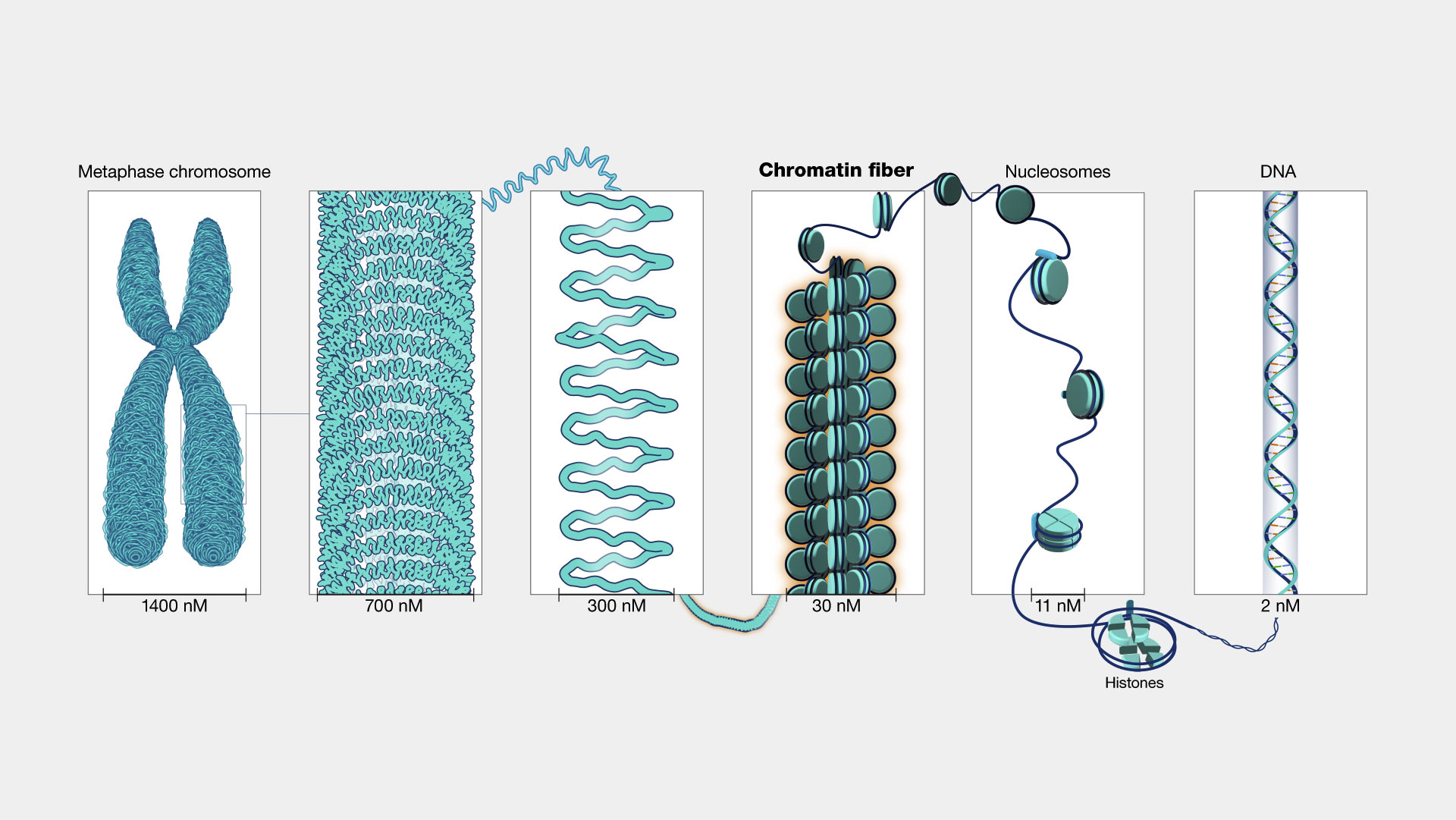
Chromatin refers to a mixture of DNA and proteins that form the chromosomes found in the cells of humans and other higher organisms. Many of the proteins — namely, histones — package the massive amount of DNA in a genome into a highly compact form that can fit in the cell nucleus.
Narration
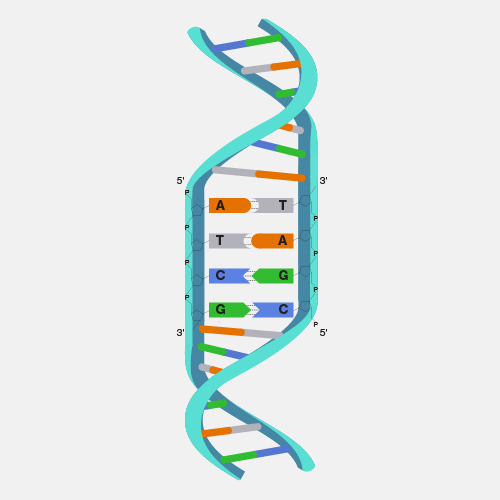
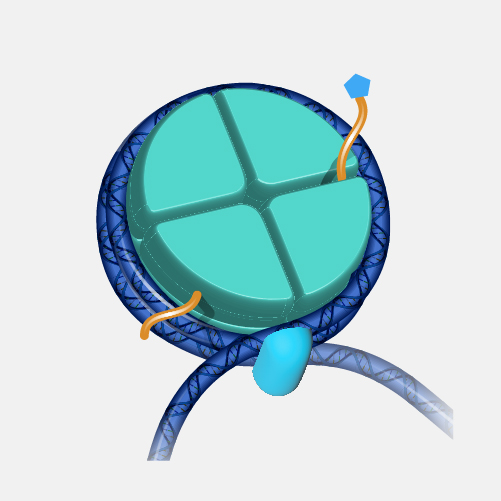
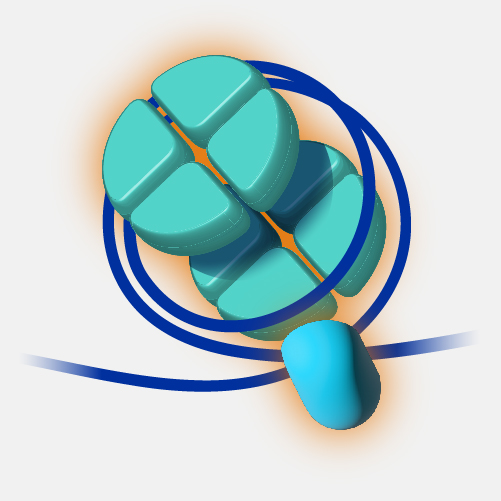
Chromatin. The total DNA in the cell is about 5 to 6 feet long which has to fit inside the nucleus of a cell in an orderly fashion. DNA molecules first wrap around the histone proteins forming beads on string structure called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes further coil and condense/gather to form fibrous material which is called chromatin. Chromatin fibers can unwind for DNA replication and transcription. When cells replicate, duplicated chromatins condense further to become a lot like chromosomes, visible under microscope which are separated into daughter cells during cell division.