Histone
Definition
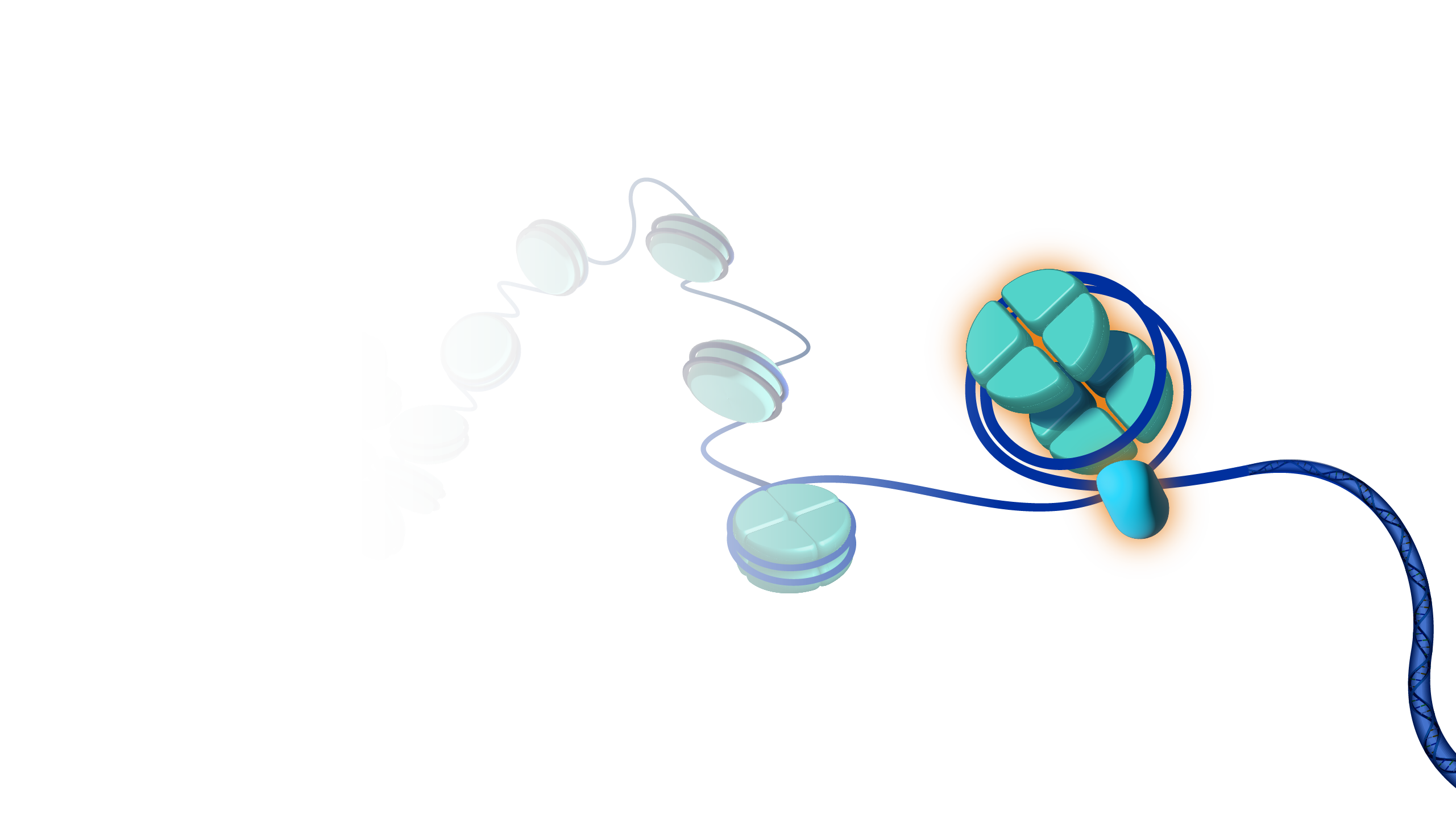
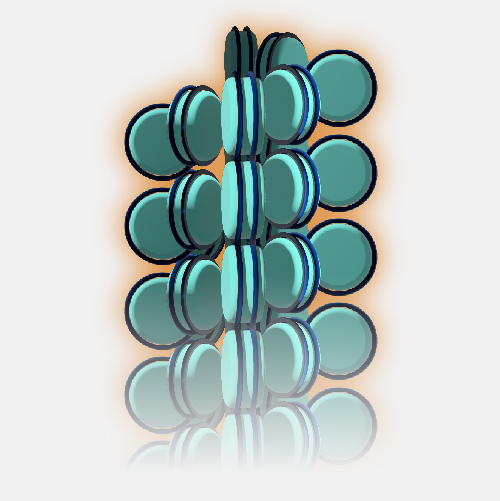
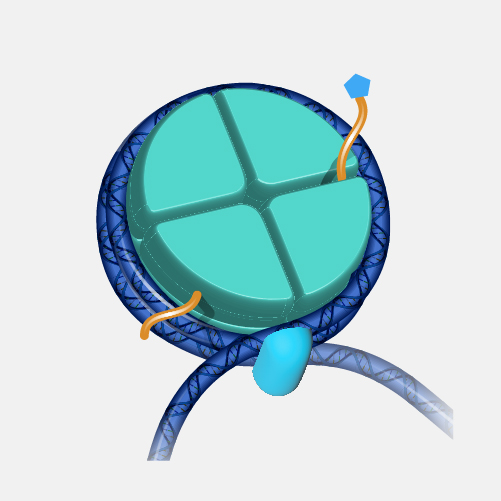
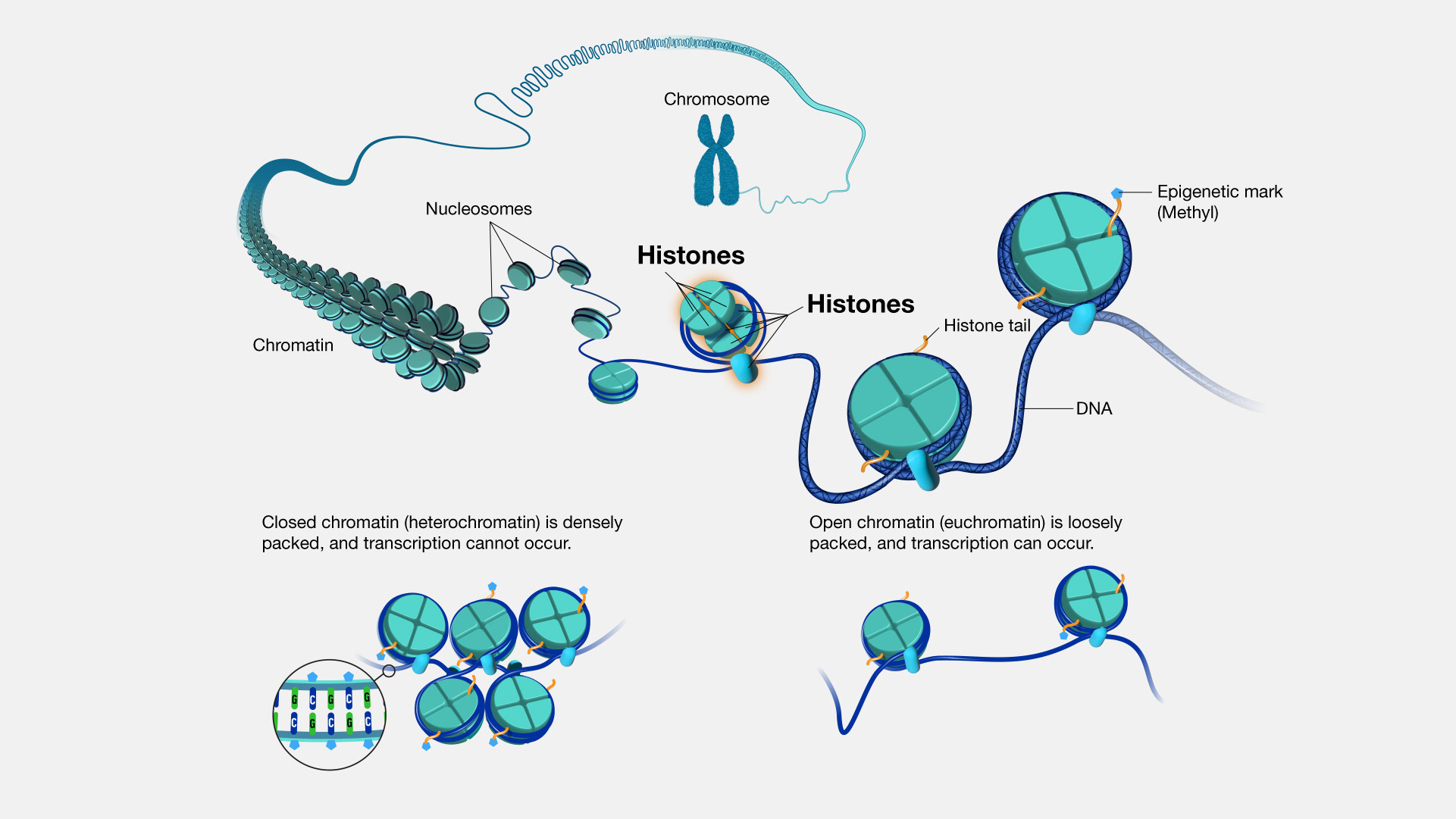
A histone is a protein that provides structural support for a chromosome. Each chromosome contains a long molecule of DNA, which must fit into the cell nucleus. To do that, the DNA wraps around complexes of histone proteins, giving the chromosome a more compact shape. Histones also play a role in the regulation of gene expression.
Narration
Histone. Eight histone proteins can come together to make up something called a nucleosome. A nucleosome is like a tiny spool that DNA can wind around. So histones play an important part in keeping the genome organized and wrapped neatly within a cell. Another cool thing about histone proteins is that they can be marked in ways that are like open or closed signs for a business. If the histones near a gene have certain marks, open signs, they can tell us that in a particular cell we're looking at a gene that is "on" — is open for business. If those histones have a different set of marks like a closed sign, those can tell us that in a particular cell a gene is "off," or closed for business. By studying histones and their marks, we've been able to learn a lot about what genes are turned on or off in different cell types. Which is very important for understanding how normal cells work and how that might be different in cells that are abnormal or contributing to disease.