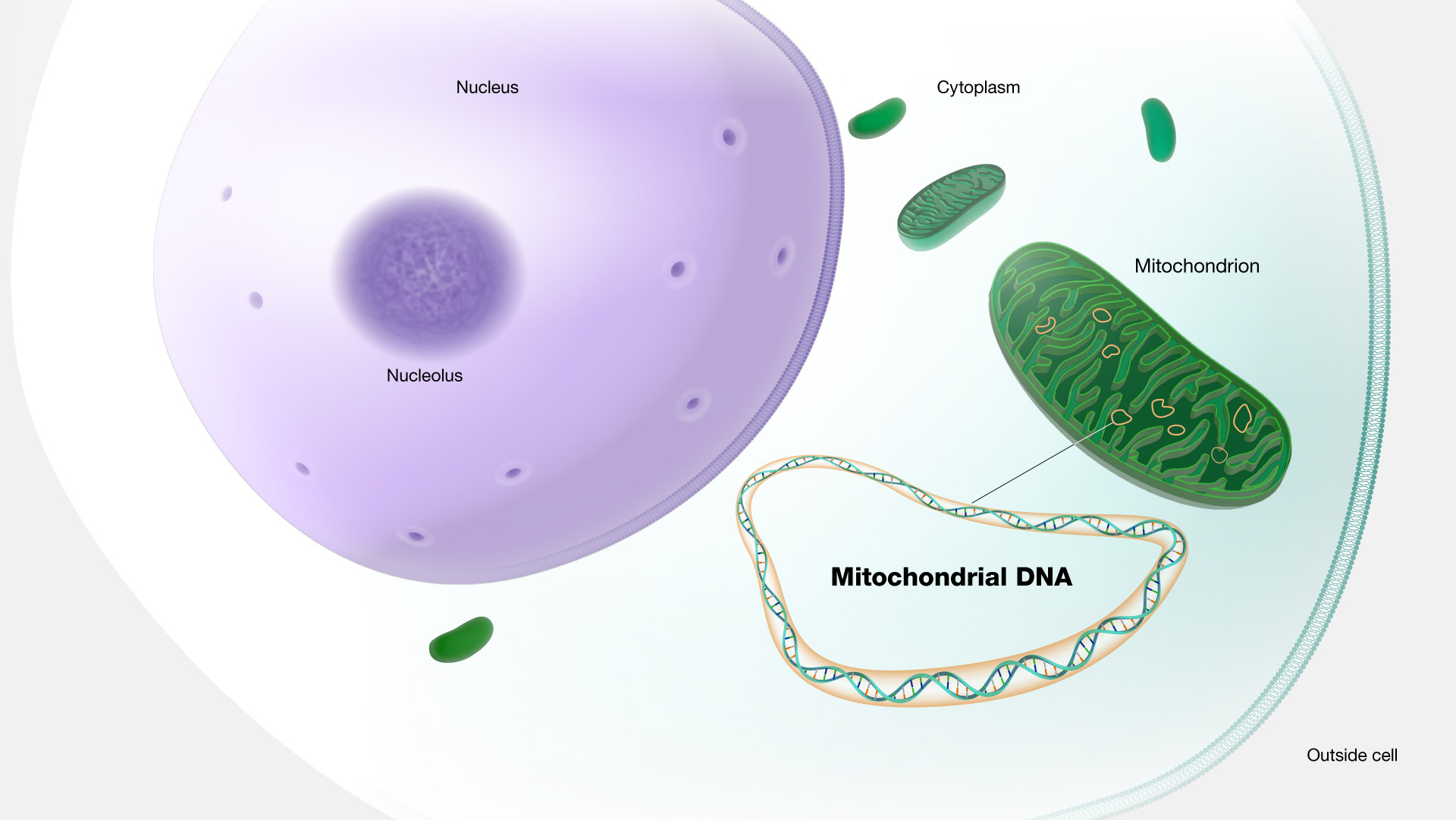
Mitochondrial DNA
Definition
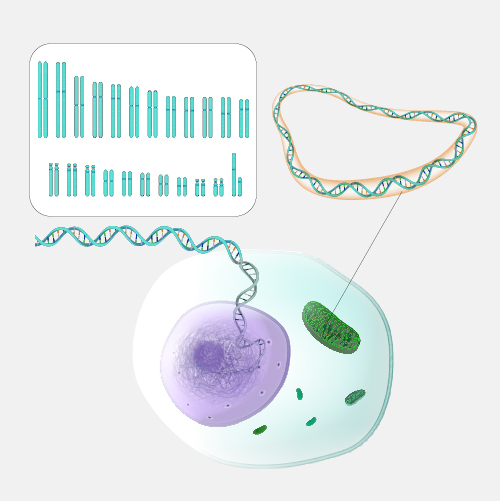
Mitochondrial DNA is the circular chromosome found inside the cellular organelles called mitochondria. Located in the cytoplasm, mitochondria are the site of the cell’s energy production and other metabolic functions. Offspring inherit mitochondria — and as a result mitochondrial DNA — from their mother.
Narration
Mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondria are organelles that produce ATP, which is the major source of energy for our cells. People who like endurance sports, like I do, think about mitochondria a lot, because a lot of what you're doing when you're training is getting your cells to make more mitochondria so that your muscles are able to cope with the demand you put on them. Mitochondria are neat because unlike other organelles, they actually have their own DNA. And because you get all of your mitochondria from your mother, they can be used to track your ancestry way, way, way back through your mother's lineage by looking at what's called your "mitochondrial haplogroup."